Prospecting & Detecting
Free / Prospecting & Detecting
Using Geologic Publications to Discover Collecting Sites
October 2018 by Peter
Note: Reporting on a mineral or fossil site does not imply permission to go onto the property. Every inch in Massachusetts and nearly everywhere else on the planet is owned by someone or some entity. You are responsible for your own actions. Speak to the landowner fact-to-face for permission to go onto the property and tell that person what you are about. Stick to that. If you are outdoor-challenged, be aware there hazards in undeveloped terrain, such as hidden pits, dangerous animals and ticks.
Okay, lecture over—let’s go onto the fun part. I understand that a person without geological knowledge could be daunted reading a geological publication. You can pick out the good stuff from a geological publication without a lot of geological knowledge.
The publication I have chosen as a model is “Geology and Mineral Resources of the Hudson and Maynard Quadrangles, Massachusetts,” US Geological Survey Bulletin 1038. As Massachusetts is an old state, much of the state was mapped long ago. This bulletin is no exception; it is dated 1956.
I chose this particular publication for a number of reasons. It covers the Bolton Lime Kiln site, and one of our members made a remarkable discovery there. More on that later.
I am going to use this site as an example of discovery although its location is well known. Beds of impure limestone were worked beginning in the colonial era for plaster material. It is best known for the occurrence of scapolite, a group of aluminosilicate minerals that includes meionite, marialite and silvialite.
The name “Bolton” is not in the title of publication. You will have to get the name of the quadrangle in which the town is located in order to find the publication you desire. In this case, either name will do to find the publication. One of the nice things about using a geologic publication to find a collecting site is you can eliminate a lot of travel. You can search using your town’s name to see if you can find a site. To find the topographic quadrangle name, search the Map Locator at www.store.usgs.gov. It turns out Bolton is in the Hudson topographic quadrangle. You can either buy the map or download the PDF. It is easier to use the PDF for what we are doing; and it is free.
 Here I will cheat a bit and use https://www.mindat.org/loc-3824.html which describes the location and mineralogy to get the geographic coordinates for the site. You can use the topographic PDF to locate the site on the map. I used the coordinates from mindat.org on Google maps.
Here I will cheat a bit and use https://www.mindat.org/loc-3824.html which describes the location and mineralogy to get the geographic coordinates for the site. You can use the topographic PDF to locate the site on the map. I used the coordinates from mindat.org on Google maps.
The site is a Conservation Area. You should check with the Bolton Conservation Commission as to the current status of collecting on the site at www.townofbolton.com/user/40/contact.
Mindat latitude and longitude coordinates are given in degrees, minutes and seconds and also in decimal degrees. Google maps will use the former format as shown below.
USGS topographic map coordinates are given in degrees decimal minutes.
 You can use this website to convert between all three types of latitude and longitude formats: www.directionsmag.com/site/latlong-converter/
You can use this website to convert between all three types of latitude and longitude formats: www.directionsmag.com/site/latlong-converter/
The decimal degrees coordinates for the Lime Kiln Site are 42.43833-71.56611. The degrees decimal minutes coordinates are 42 26.2998 N 71 33.9666 W. On the topographic map, note that my coordinates are a bit off. One needs a surgeon’s hand to be precise with the mouse.
You can compare this with the Google satellite map.
Great! We found the mineral locality site in Bolton. As noted, this publication is out-of-print. You can download it by searching for the Hudson quadrangle at ngmdb.usgs.gov/ngmdb/ngmdb_home.html
 You will find that you can only download the bedrock geologic map, which can be found at: ngmdb.usgs.gov/Prodesc/proddesc_20626.htm
You will find that you can only download the bedrock geologic map, which can be found at: ngmdb.usgs.gov/Prodesc/proddesc_20626.htm
You can also search for depository libraries to borrow the publication here: catalog.gpo.gov/fdlpdir/FDLPdir.jsp?st_12=MA&flag=searchp
or search in www.worldcat.org
Another source is play.google.com/books/reader?id=4aYPAAAAIAAJ&printsec=frontcover&output=reader&hl=en&pg=GBS.PP1
As for me, I prefer the real deal. I got a copy through my public library. I went through the bulletin, picking out portions that I thought would be interesting to a collector. One idea is to collect material from your area and build a display. Here is what I found:
Pages 9-11: Knots of epidote
Page 17: Xenoliths
Page 18: Plant fossils
Page 24: Folding
Page 27: Andalusite chiastolite sillimanite
Page 33: Garnet sillimanite apatite
Page 38-39: Marble beds pegmatite
Pages 98-100: Marble
The title of this article is geologic maps, so where are the geologic maps? There are three maps in the pocket of the publication. They are as follows:
Plate 1. Map and sections showing bedrock geology of the Hudson and Maynard Quadrangles, Massachusetts. (Sections are diagrams portraying a cut into the earth, but those are not our concern.)
Plate 2. Map showing surficial geology of the Hudson and Maynard Quadrangles, Massachusetts. (Surficial geology deals with the types of sand and gravel deposits left by the glaciers of the Ice Age. Those also are not of our concern. What we want to look at are the quarry symbols and bedrock outcrops shown on the map.)
Plate 3. Melt water drainage-sequence of the Hudson and Maynard Quadrangles, Massachusetts. (This map shows the direction of water flow as the glaciers were melting. It is very cool, but not essential to our purpose. We will ignore this map.)
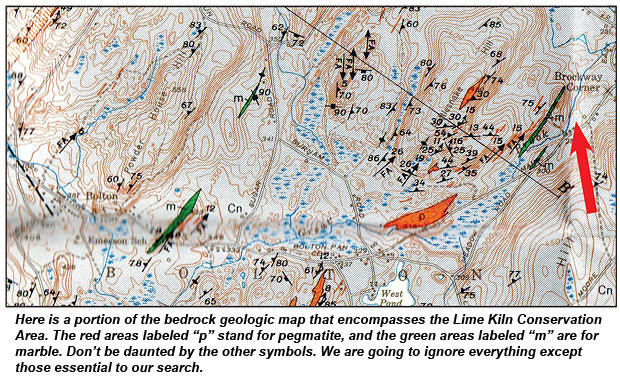
In the upper right corner of the bedrock geological map, Brockway Corner is labeled (a large red arrow has been added to direct the reader). Trending to the southwest is a green lens labeled “m,” which stands for marble. How do I know that? There is a legend on the map that shows the various rock types on the whole map. You will see in the square for the Nashoba Formation the green and “m” for marble symbol. There is also a red color and “p” that denotes pegmatite.
That green lens by Brockway Corner is the Lime Kiln Conservation Area and includes the well-known deposit. But look—to the west are two more green lenses. People have beaten the Lime Kiln area to pieces. These two may be pristine occurrences that need to be investigated, and the red lenses labeled “p” for pegmatite as well!
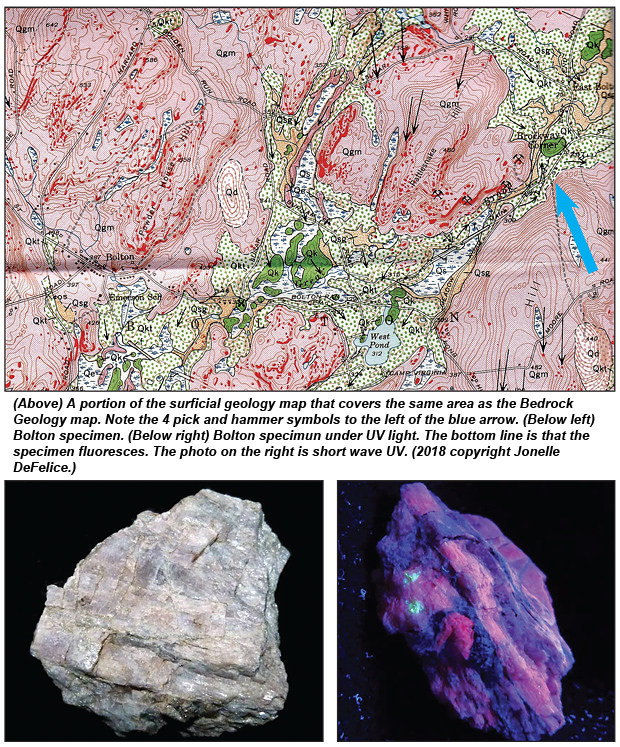
On the surficial geology map, by the Brockway Corner label (a large blue arrow has been added) you will note four pick and hammer symbols representing quarries. The well-known quarry is almost certainly the second symbol down from Brockway Corner. Undoubtedly others, including me, have concentrated on the quarry not knowing there are three others. (See the red splotches representing rock outcrops on the Surficial Geology map.) It would be beneficial to correlate the outcrops with the marble and pegmatite lenses noted before. A lot of time can be saved in the field if GPS coordinates were measured with the correlations.
Now I will introduce to you Jonelle DeFelice. She describes herself as a novice. She has graciously allowed me to describe her discovery at the Bolton quarry. (You can get the back story by searching for Bolton on the Boston Mineral Club page of Facebook.)
I am, at best, a casual mineralogist. I don’t know how well this fluorescent fact is known about the Bolton site. The blue is meionite, red is calcite, and the green speck is willemite. Meionite is the calcium-rich end member of the scapolite series. It is very similar and often indistinguishable from marialite, the other end member of the series. Intermediary forms of meionite and marialite are frequent, and these are classified simply as scapolite.
This is my identification so a correction may be in order. Without the UV a person could call the whole specimen scapolite.
Here is the payoff! With a strong UV at night, the Bolton quarry might light up. Other less known quarries could do the same. This may be undiscovered territory. Remember: there are landowner and outdoor hazards, particularly at night.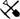
© ICMJ's Prospecting and Mining Journal, CMJ Inc.